Covering for the Future
by hanna_kowal | September 19, 2025 9:57 am
 [1]
[1]Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) resin-based coatings have set a high benchmark in long-term metal protection, proving effective across various applications—from architectural panels and roofing to industrial equipment. These factory-applied finishes are chosen by architects, specifiers, and building owners for their ability to deliver consistent performance, aesthetic durability, and environmental resilience over decades of service.
 [2]
[2]AI-generated image via ChatGPT with DALL-E, based on an original photo submitted by Tex-Cote and Arkema
One of the key advantages of PVDF coatings is exceptional color retention. These finishes resist fading caused by prolonged UV exposure, helping metal surfaces maintain vibrancy over time. Their chemical resistance offers
robust protection from acid rain, salt spray, and industrial pollutants, making them well-suited for harsh environmental conditions.
Durability is another defining trait. PVDF coatings perform reliably in extreme climates, resisting cracking, peeling, and degradation under high heat, humidity, or subzero temperatures. Their longevity also supports sustainable building practices by reducing the frequency of recoating, minimizing lifecycle impacts.
Finally, many PVDF coatings incorporate heat-reflective formulations that reduce thermal absorption, making them a preferred solution for cool roofing systems and cool wall systems, providing energy-efficient facade designs.
Molecular structure supports long-term performance
The durability and longevity of PVDF-based polymeric coatings stem from the strength of their carbon-fluorine bonds. These bonds resist environmental degradation, preserving film thickness and shielding the coating’s infrared-reflective (IR) pigments much longer than other resin-based coatings. This molecular resilience supports a range of protective properties, including solar reflectance, dirt shedding, resistance to algae and mildew, color and gloss retention, and resistance to chalking and fading. Dirt and biological buildup can significantly diminish solar reflectance, making these self-cleaning characteristics essential to long-term energy performance.
 [3]
[3]AI-generated image via ChatGPT with DALL-E, based on an original photo submitted by Tex-Cote and Arkema
Field-applied coatings expand repaint potential
Water-based PVDF coatings offer a high-performance alternative that does not require high-temperature baking. These formulations are designed for air-dry, field-applied use, making them well suited for repaints or site-applied applications. The coatings deliver weather resistance comparable to traditional factory-applied PVDF systems and adhere effectively to various aged substrates—including metal, plastics, concrete, fiber cement, stucco, EIFS, and previously coated surfaces.
Durable solutions for challenging metal environments
Architects have long specified factory-applied PVDF-based coatings for their proven colorfastness and weathering performance on exterior metal components such as window frames and doors. Newer air-dry formulations offer comparable durability in field-applied conditions, expanding their use to repaints of walls and sloping roof surfaces. These coatings resist degradation from prolonged heat exposure and perform well in hot, humid climates, where thermal cycling can otherwise cause adhesion failure, color loss, and coating breakdown. Compared to conventional acrylic or elastomeric coatings, water-based PVDF coatings exhibit significantly greater thermal stability and less moisture vapor drive, helping maintain color, gloss, and film integrity over longer periods.
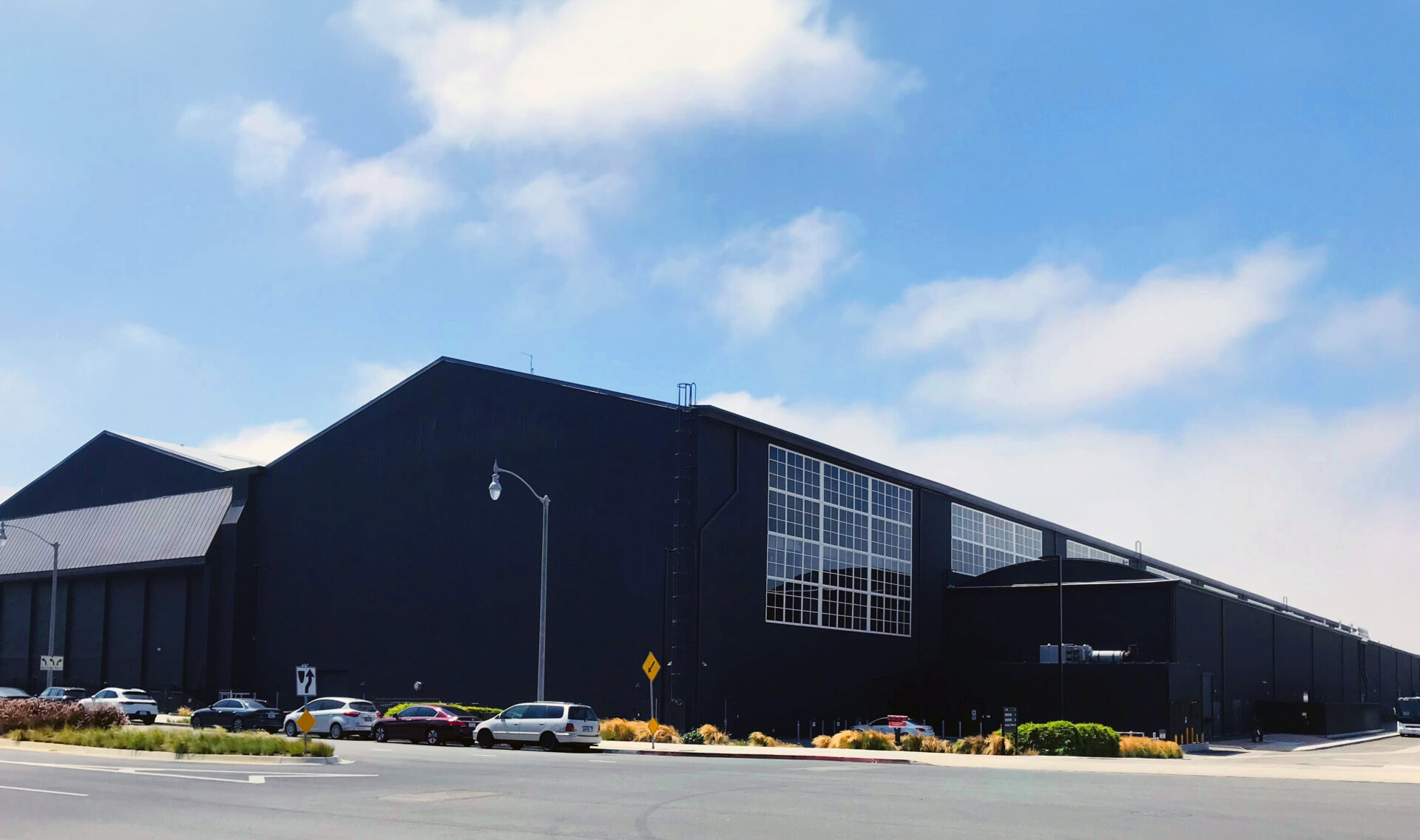
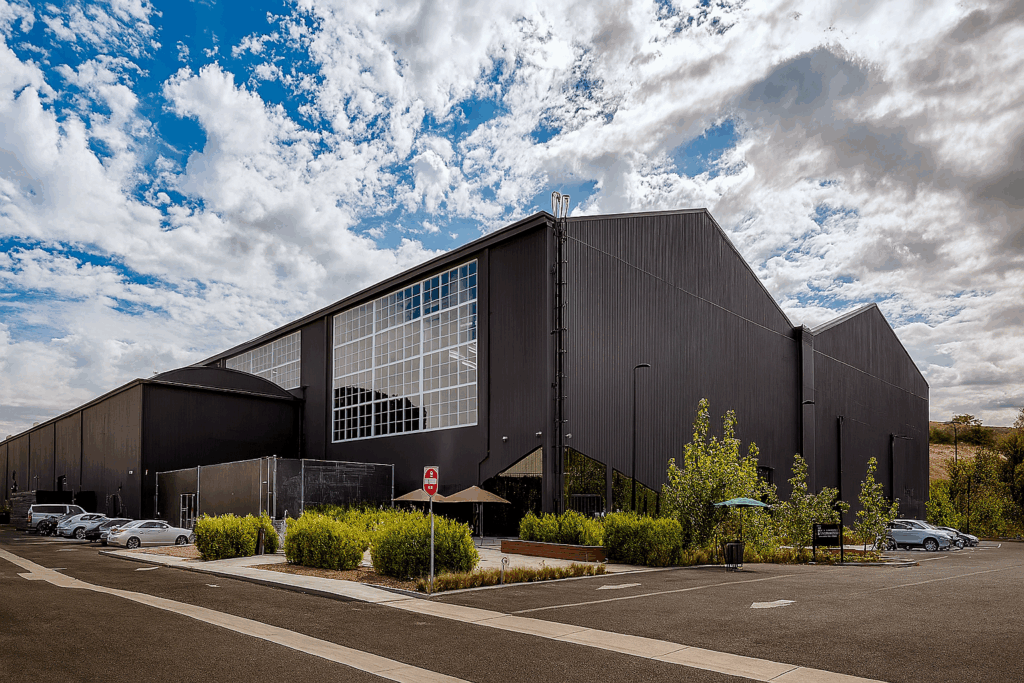
Case study: Coastal retrofit with reflective metal finish
A historic aircraft hangar near the Los Angeles, Calif., coast has been restored and converted into office space for a large technology company. Located within a few miles of the shoreline, the building’s metal facade required a finish capable of withstanding exposure to marine conditions and solar radiation.
 [4]
[4]Photos courtesy Tex-Cote and Arkema
A water-based PVDF coating, including a dark custom color, was applied to the exterior. The coating was selected for its resistance to ultraviolet degradation and its ability to retain color over time—important qualities in climates with prolonged sun exposure, where dark finishes are particularly susceptible to fading and chalking.
In this application, the coating increased the building’s total solar reflectance (TSR) by 320 percent improvement. Increased solar reflectance contributes to lower surface temperatures, longer coating life, reducing interior cooling loads and decreasing demand on HVAC systems.
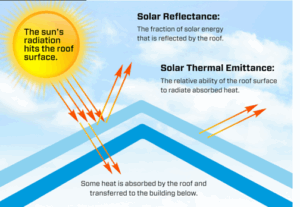 [5]
[5]Cool-surface coatings are designed to reduce solar heat gain through the building envelope, which can help maintain lower indoor temperatures compared to less reflective surfaces. For commercial buildings, where cooling accounts for an estimated 15 percent of total electricity use, this can result in measurable energy savings.
This retrofit illustrates how water-based PVDF systems may be used on existing buildings to address performance and aesthetic considerations in demanding environments.
A future-focused finish for the building envelope
As performance demands on the building envelope continue to rise, PVDF coatings remain a reliable and adaptable solution for metal architecture. Their proven resistance to environmental stressors, long-term colorfastness, and expanding application options—including air-dry, field-applied formulations—position them well for new construction and repaint projects. Whether specified for energy efficiency, aesthetics, or longevity, PVDF coatings will continue to play a key role in advancing durable, high-performance metal facades and roofing systems.
Terry Wallace is a National Association of Corrosion Engineers (NACE) Level III Coating Inspector, USGBC LEED-accredited professional, and Tex-Cote LLC’s vice president of sales. He was a co-owner of coatings manufacturer Chemprobe Technologies Inc., which was acquired by Tnemec Company, where he held various sales and management roles for more than 20 years.
- [Image]: https://www.metalarchitecture.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/09/Reflect-Tec-by-Tex-Cote_LA-Hanger-Office-Project_AFTER-PHOTO.jpg
- [Image]: https://www.metalarchitecture.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/09/ChatGPT-Image-Aug-7-2025-07_36_16-PM.png
- [Image]: https://www.metalarchitecture.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/09/ChatGPT-Image-Aug-7-2025-07_41_24-PM.png
- [Image]: https://www.metalarchitecture.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/09/Reflect-Tec-by-Tex-Cote_LA-Hanger-Office-Project_APPLICATION.jpg
- [Image]: https://www.metalarchitecture.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/09/Picture1.png
Source URL: https://www.metalarchitecture.com/articles/features/covering-for-the-future/